ReentrantLock 是 Lock 的一个子类,和 synchronize 一样称之为可重入锁,它有着和 synchronize 同样的内存语义,但功能比 synchronize 功能更多,使用起来更为灵活。
可重入锁:能够支持对资源的重复加锁,一个典型例子就是同一个类的 synchironized 方法内可以调用本类其他的 synchronize 方法。
使用 ReentrantLock 实现同步
代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| public class ReentrantLockThread implements Runnable {
public static int num = 0;
private static final Lock LOCK = new ReentrantLock();
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
LOCK.lock();
try {
num++;
}finally {
LOCK.unlock();
}
}
}
}
|
Run 类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| public class Run {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ReentrantLockThread lockTest = new ReentrantLockThread();
Thread t1 = new Thread(lockTest);
Thread t2 = new Thread(lockTest);
t1.start();
t2.start();
t1.join();
t2.join();
System.out.println(ReentrantLockThread.num);
}
}
|
结果:
多次执行都是20000。
ReentrantLock 可以完全替代 synchronize 来使用,而且更好用。
ReentrantLock 其他功能
尝试非阻塞地获取锁:当前线程尝试获取锁,如果这一时刻锁没有被其他线程获取到,则成功获取并持有锁。
能被中断地获取锁:获取到锁的线程能被中断,抛出中断异常并释放锁。
超时获取锁:在指定的截止时间之前获取锁,如果在指定的时间内仍未获取锁则返回,避免死锁。
尝试非阻塞地获取锁
对应 API: tryLock() 和 tryLock(long time, TimeUnit unit),这两个 API 具体的区别前面已经提到,这里不再重复描述。
代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| public class TryLockTest implements Runnable{
private static final ReentrantLock LOCK = new ReentrantLock();
@Override
public void run() {
if(LOCK.tryLock()){
System.out.println("线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"获取锁成功!");
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
}catch (Exception e) {
}finally {
LOCK.unlock();
}
}else {
System.err.println("线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"获取锁失败!");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TryLockTest tryLockTest = new TryLockTest();
Thread t1 = new Thread(tryLockTest, "t1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(tryLockTest, "t2");
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
|
打印结果:
这是因为t1获取锁后,sleep 3秒,这期间仍然持有锁不释放,t2去尝试获取锁时自然获取不到。
可被中断地获取锁
API: lockInterruptibly();
代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
| public class LockInterruptiblyTest implements Runnable {
private String type;
private static final ReentrantLock LOCK_A = new ReentrantLock();
private static final ReentrantLock LOCK_B = new ReentrantLock();
public LockInterruptiblyTest(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
if ("a".equals(type)) {
LOCK_A.lockInterruptibly();
Thread.sleep(1000);
LOCK_B.lockInterruptibly();
}else if ("b".equals(type)){
LOCK_B.lockInterruptibly();
Thread.sleep(1000);
LOCK_A.lockInterruptibly();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"被中断");
} finally {
if(LOCK_A.isHeldByCurrentThread()){
LOCK_A.unlock();
}
if(LOCK_B.isHeldByCurrentThread()){
LOCK_B.unlock();
}
}
System.err.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"退出!");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LockInterruptiblyTest testA = new LockInterruptiblyTest("a");
LockInterruptiblyTest testB = new LockInterruptiblyTest("b");
Thread tA = new Thread(testA);
Thread tB = new Thread(testB);
tA.start();
tB.start();
}
}
|
tA.interrupt();先注释掉,运行程序,必然产生死锁,因为双方都持有对方想要的锁不释放,将tA.interrupt();代码放开,再次运行,打印:
程序结束,验证 lockInterruptibly()方法,获取锁的线程可以被中断后并释放锁。
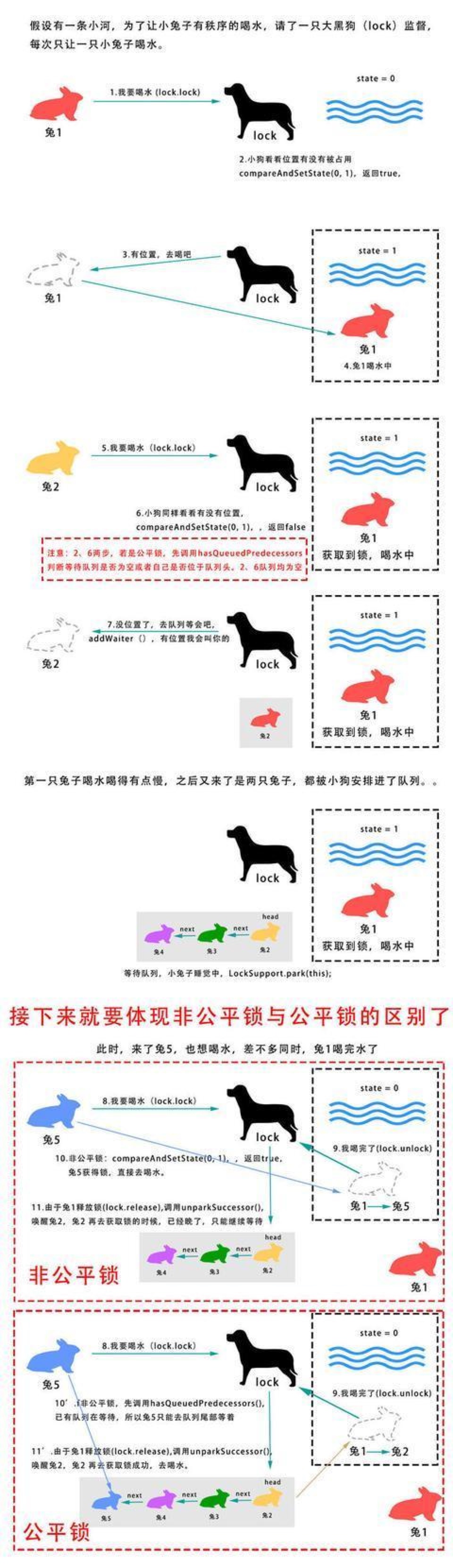
公平锁和非公平锁
ReentrantLock 还支持公平锁和非公平锁,可以先了解下什么是公平锁和非公平锁:
公平锁:保障了多线程下各线程获取锁的顺序,先到的线程优先获取锁。
非公平锁:各线程获取锁不是顺序而是随机的。
从网上找了一副图很形象地描述了什么是公平锁和非公平锁: